If you’re looking to push your container game a bit, you can also convert your own ISOs (or ISOs you trust) into Docker Images. Jack Wallen shows you how.

Image: Jack Wallen
In your quest to build the perfect cloud container application, you might have found the available images either don’t include all the tools you need, include too many tools, or simply cannot be trusted. To that end, you might opt to create your own images from any given ISO you’ve either downloaded or created.
But how do you do that? I’m going to show you.
SEE: Implementing DevOps: A guide for IT pros (free PDF) (TechRepublic)
What you’ll need
I’m going to demonstrate on Ubuntu Unity, but this process can be done on just about any Linux distribution. You’ll need a desktop Linux installation up and running, a user with sudo privileges, and an ISO to convert.
How to install the necessary tools
First, you need to install squash-fs. To do this, open a terminal window and issue the command:
sudo apt-get install squashfs-tools -y
You might find the squashfs-tools already installed. If so, move on to the next installation–Docker.
To install Docker on your machine, go back to the terminal and issue the command:
sudo apt-get install docker.io -y
Once Docker is installed, start and enable the service with the commands:
sudo systemctl start docker sudo systemctl enable docker
Add your user to the Docker group with the command:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
Make the system aware of the new group addition with the command:
newgrp docker
How to mount the ISO
Now we need to mount the ISO you downloaded (or created yourself). I’ll demonstrate with the Ubuntu Server 20.04 ISO. Before you mount the ISO, create two new folders with the command:
mkdir rootfs unsquashfs
To mount the ISO image into the rootfs folder, issue the command:
sudo mount -o loop ~/Downloads/ubuntu-20.04-live-server-amd64.iso ~/rootfs
The above command will mount the image as read-only, so you can ignore the warning.
We need to locate the directory housing the filesystem.squashfs file. To do that, change into the rootfs directory with the command:
cd ~/rootfs
Locate the file with the command:
find . -type f | grep filesystem.squashfs
On the Ubuntu server ISO, that file should be located in the casper directory.
Now that we know where the filesystem.squashfs file is, we can extract the necessary filesystem files from the rootfs directory into the unsquashfs directory with the commands:
cd ~/ sudo unsquashfs -f -d unsquashfs/ rootfs/casper/filesystem.squashfs
Remember to replace casper with the directory housing your ISO filesystem.squashfs file.
Depending on the speed of your machine, the above command should happen pretty quickly and will end with a report of how many files, directories, symlinks, devices, and fifos were created (Figure A).
Figure A
” data-credit rel=”noopener noreferrer nofollow”>
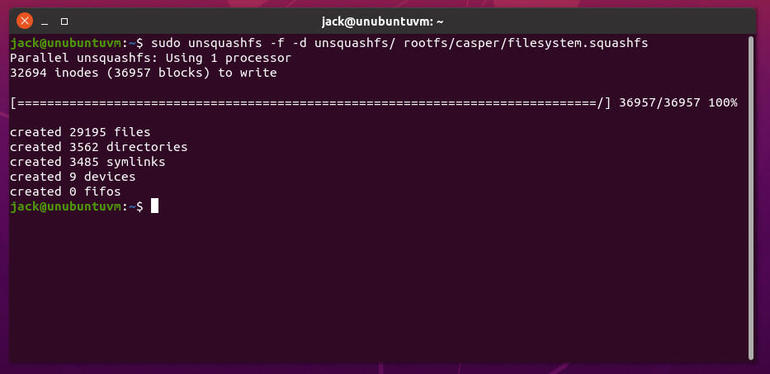
We’ve successfully extracted the necessary files.
How to compress and import the image
Finally, we can compress and import the image using Docker. To do this, issue the command:
sudo tar -C unsquashfs -c . | docker import - IMAGENAME/TAG
Where IMAGENAME is the name you want to give the image and TAG is a tag for the image. When the process completes, you’ll see an sha256 hash for the image printed out (Figure B).
Figure B
” data-credit rel=”noopener noreferrer nofollow”>
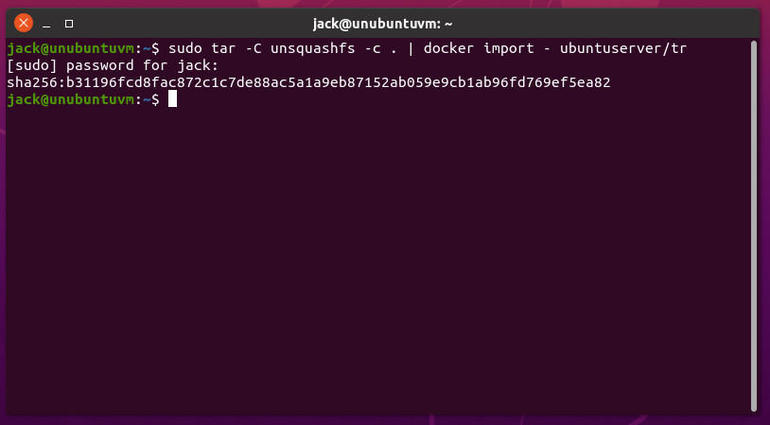
Our image sha256 hash indicates a successful import.
To see your Docker image listed, issue the command:
docker images
Your newly crafted image should appear (Figure C).
Figure C
” data-credit rel=”noopener noreferrer nofollow”>
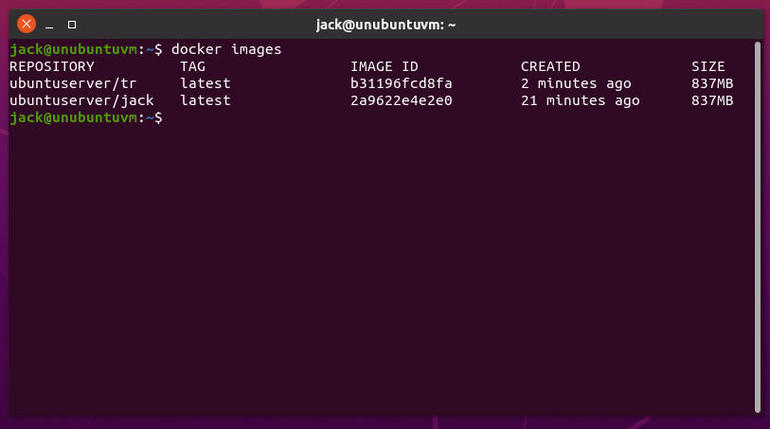
Our new Docker image is ready to be used for deploying containers.
And that’s all there is to creating your own Docker images from downloaded ISOs. Congratulations, you’re one step closer to ensuring your containers are built from ISOs you’ve either created yourself or have vetted and trust.
Also see
Source of Article



